Multi-tenant Web Apps with Laravel


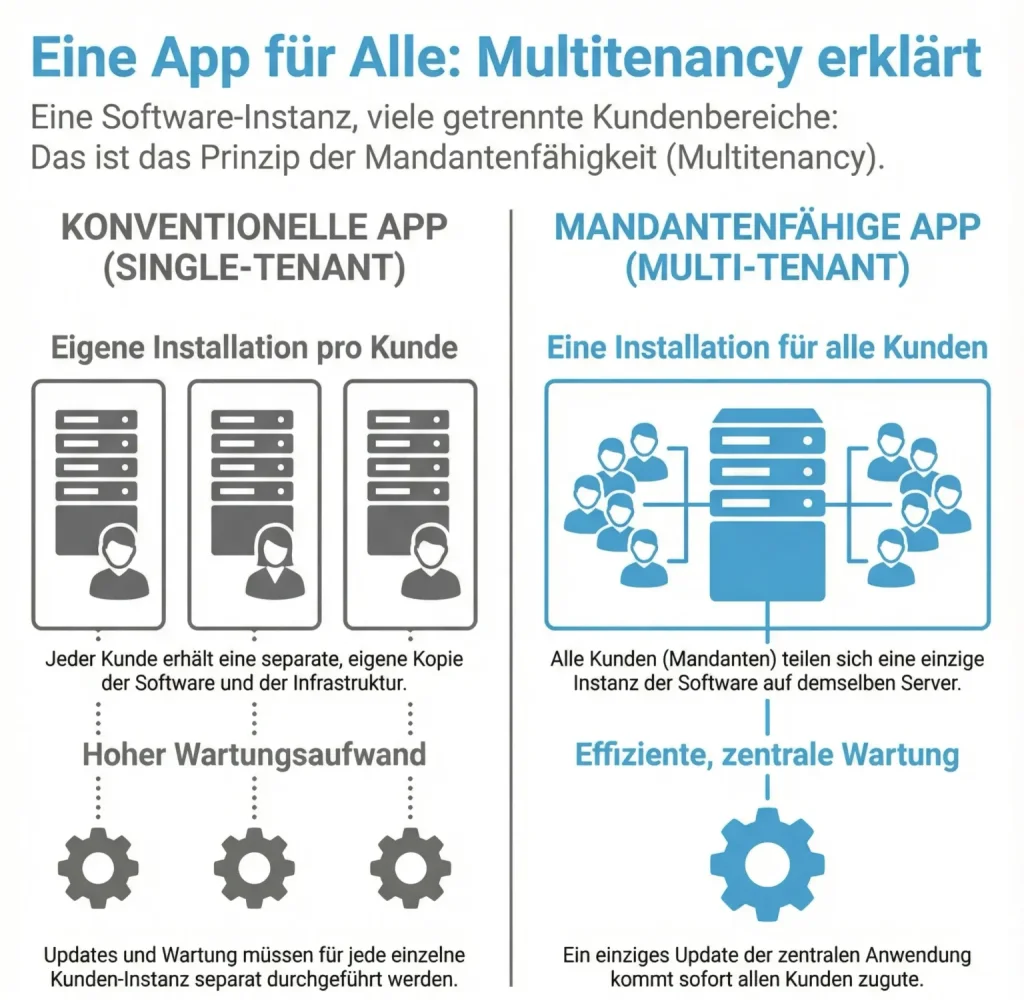
Multi-tenancy means that a single software application can serve multiple customers simultaneously -- each with their own data and settings.
In a multi-tenant environment, all customers use the same application but only see their own data. This architecture is especially popular with SaaS products.
The biggest advantage for you: reduced development and maintenance costs. Updates only need to be deployed once and are immediately available to all users. Your budget stays predictable while your software scales with every new customer.
What Is Multi-Tenancy?
Think of it like an office building: each company has its own office with its own key, but they share elevators, heating, and building management. Multi-tenant software works the same way -- each customer (tenant) has their own secure space while sharing the technical infrastructure with others.
Each tenant has their own area with separate data, settings, and users. This allows you to run a customer portal or a custom CRM system that serves many different companies at once -- without them ever seeing each other's data.
What Is Multi-Tenant Software Used For?
With multi-tenant software, you serve many customers with a single application. Each customer group works in their own protected space -- completely isolated from others. Different customers can use the same software without their data ever being mixed together.
Which Multi-Tenant Architecture Is Right for You?
The right architecture depends on your specific project: How sensitive is the data? Are there legal requirements? How many tenants do you expect? We clarify these questions together before development begins.
There are fundamentally two approaches: a shared database for all tenants, or separate databases per customer. In most cases, the shared database is the better choice -- it is easier to maintain and more cost-effective to operate.
Multi-Tenancy with a Shared Database
With this approach, all tenants store their data in a single shared database. Separation is achieved through a unique identifier -- much like filing folders in a shared cabinet, each clearly labelled.
Technically, every record is assigned an organisation identifier. This ensures that each tenant only ever sees their own data -- the separation happens automatically in the background.
Important to know: the data is physically stored in the same location. This is perfectly fine in the vast majority of cases -- as long as no special legal requirements mandate strict physical separation.
„Is a shared database less secure? No -- if the software is properly developed. Virtually every online shop works on the same principle. What matters is software quality and thorough test coverage.”
Separate databases are no substitute for clean development work -- they only make the project more expensive and more complex.
Advantages of Shared-Database Multi-Tenancy
With Laravel as the foundation, you benefit from a mature framework that optimally supports multi-tenant systems.
No deep framework modifications are needed, so updates remain straightforward. You can keep your system current and secure long-term.
New customers can be onboarded in seconds -- a simple registration process is all it takes. No complex setup, no manual steps.
Multi-Tenancy with Separate Databases
With this approach, each tenant receives their own database. Data is physically separated from other tenants. This may be necessary when strict legal regulations demand it -- for example, with particularly sensitive health or financial data.
„Caution -- this is a one-way street. Separate databases are significantly more complex and expensive. Once chosen, the decision is nearly impossible to reverse.”
That is why we carefully evaluate at the start of every project whether a separate database architecture is truly required. Without compelling requirements, we advise against it.
Using Multiple Databases with Laravel
When physical data separation is unavoidable, Laravel supports this architecture as well. A separate database is created for each tenant. This provides maximum isolation -- but comes with significantly higher effort.
For this approach, we recommend the proven "Multitenancy" package by Spatie. It greatly simplifies managing separate databases and provides useful day-to-day tooling.
Challenges of a Multi-Database Setup
Tenant context awareness: The software must always know which tenant is currently active. This affects every part of the application -- an additional layer of complexity that requires careful implementation.
Customer onboarding: Setting up new customers becomes more involved because a separate database must be provisioned for each tenant. While this can be automated, it adds infrastructure complexity and cost.
Scaling bottlenecks: Without automation, new tenants must be created manually -- a process that quickly becomes a bottleneck as your customer base grows.
The Real Benefits of Multi-Tenant Software
The biggest win is scalability: with each new customer your revenue grows, while operating costs remain nearly constant. At the same time, every tenant benefits from improvements you make in one central place.
Implementation with Built-In Laravel Features
Since separate databases are only necessary in exceptional cases, we focus on the proven single-database solution.
Laravel provides everything you need for a multi-tenant system -- no additional packages required. At its core is an "organisations" table to which all other data is linked.
All application data is associated with this organisation. Through automated testing, we ensure that no tenant can ever access another tenant's data. Test Driven Development (TDD) is essential for multi-tenant systems -- the investment in thorough testing pays off in the long run.
Laracon Talk on Multi-Tenancy
At Laracon 2017, Tom Schlick delivered a talk on multi-tenancy in Laravel.
Our Recommendation
A shared database is the right choice for most projects. It enables fast growth, simple maintenance, and keeps costs manageable.
Unless legal requirements mandate physical data separation, we recommend the single-database solution. Want to build multi-tenant software? Get in touch -- we are happy to advise you.
Further reading: